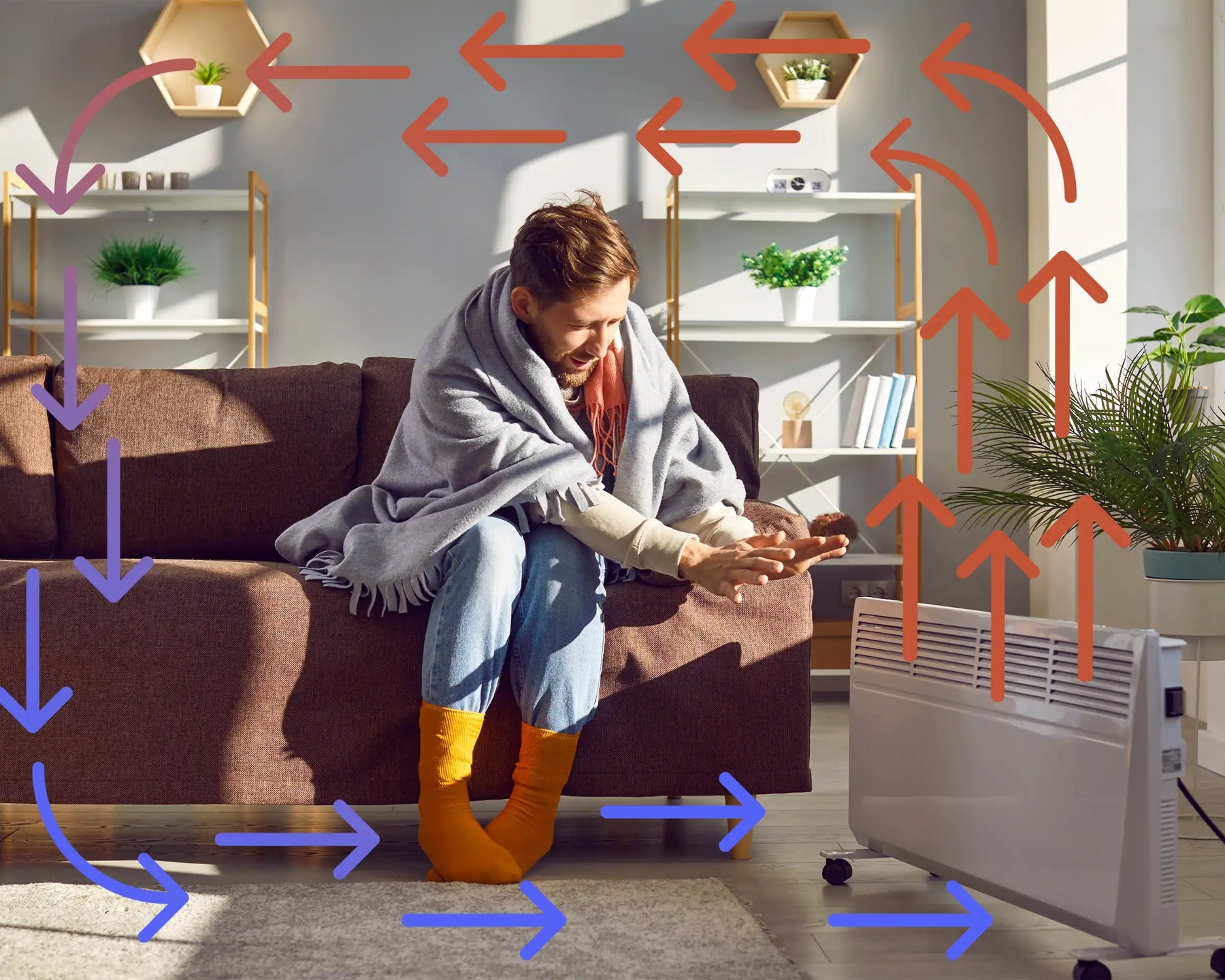
The easiest way to understand how IR works is to stand outside on a nice sunny day (not always easy in the UK!). If you stand in full sunshine you feel warm – but where is the warmth coming from? No boiler is running. No electric or convection heaters are on. Yet stay still and you’ll keep on warming-up.
It’s quite simple. The radiant heat of the sun is hitting your body and warming you up. And it’s IR radiation – the good radiation, not the ultra-violet radiation that gives you sunburn. In terms of technology IR heating is the latest and newest way to keep your home or office warm.
Unlike conventional heaters, where the heat goes into the air but quickly dissipates, IR directly warms up humans, animals, and the objects around you. It works both indoors and out.
What is Infrared Heating?
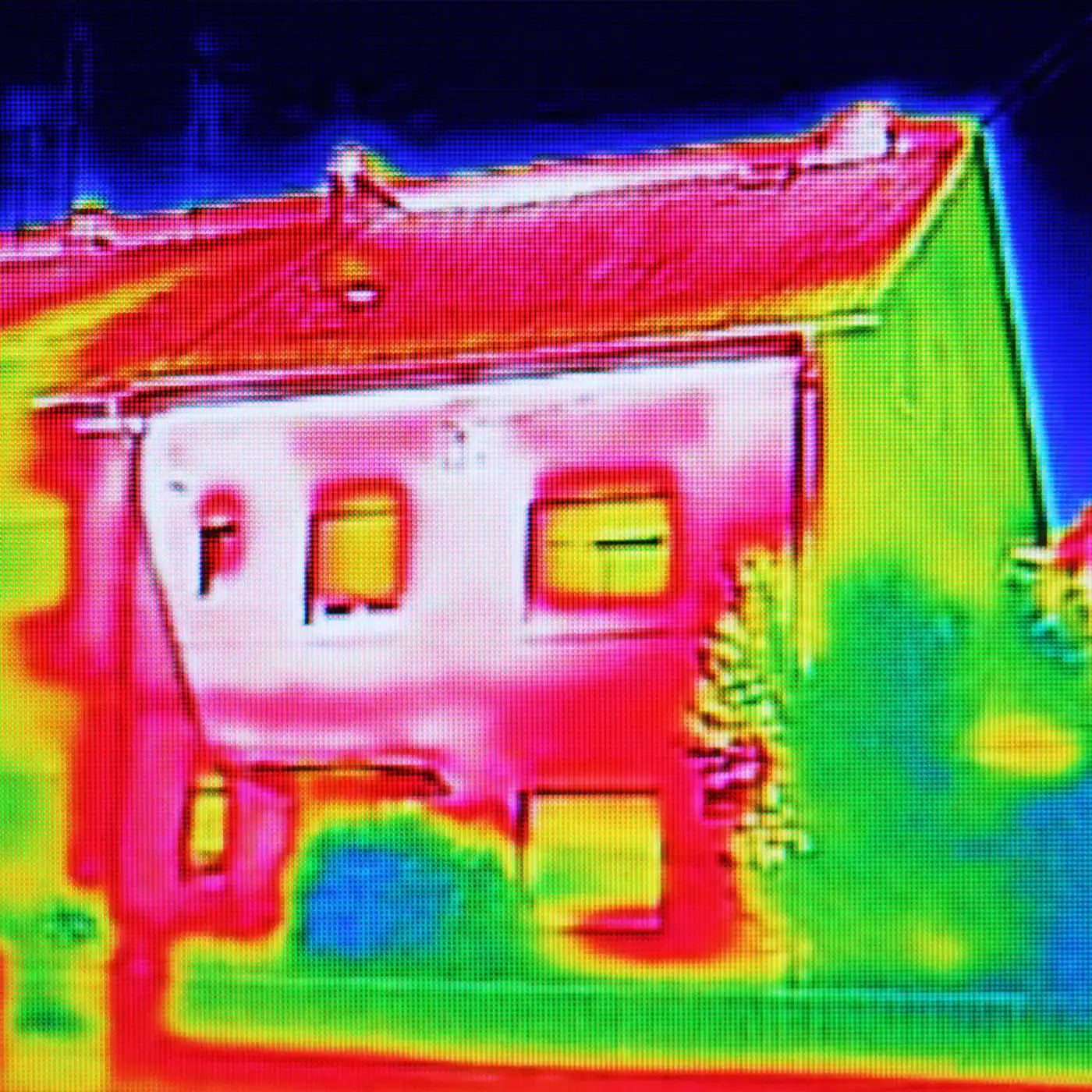

Thermal image on Residential building
Thermal or infrared radiation enables us to detect heat signatures emitted by objects and observe them even in darkness. It plays a crucial role in various fields, including night vision technology, medical diagnostics, and environmental monitoring.
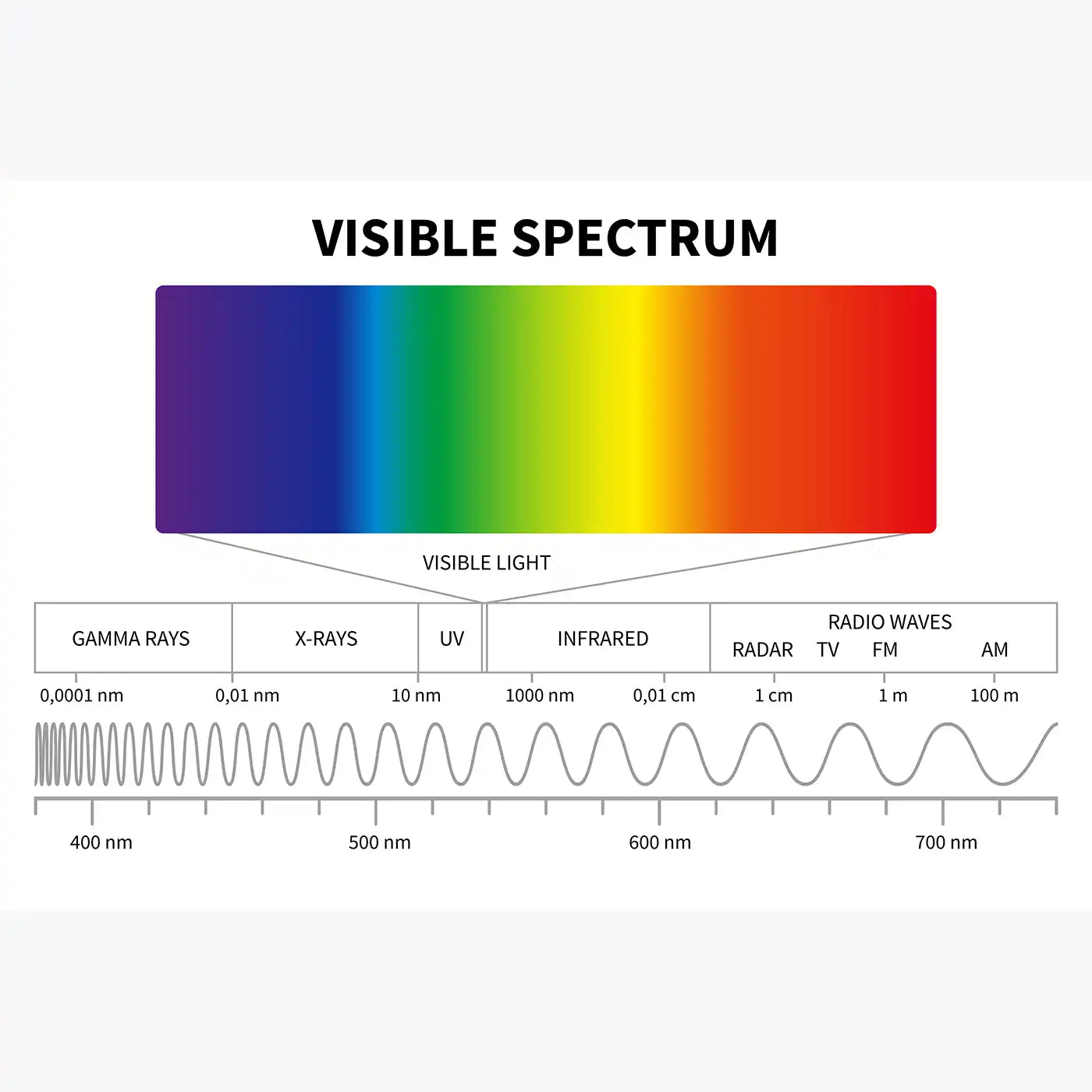
Visible Spectrum
The visible spectrum refers to the range of electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, spanning from violet to red light. This portion of the electromagnetic spectrum is responsible for the colours we perceive in the world around us.
The Basics
Infrared heating is the latest and newest in technology to keeping your home or office warm.
Conventional heaters such as oil-filled heaters, storage heaters and even boiler systems use air to move heat around the room. Since hot air rises, heat manages to escape from your homes, which means you would have to keep the heater on for longer periods of time to maintain a certain degree of heat. Not only this, but it creates a stuffy environment giving you respiratory issues and scratchy eyes. Infrared heaters use invisible light to heat up humans, pets and objects within a room, minimising heat loss completely while also improving your health and creating a humid-free environment. The heat (light) bounces from surface to surface and keeps the heat within your home. Since it is radiant heating, the rays reach in more areas which gradually reduces cold spots within the room.
Far infrared (FIR) heating and near infrared (NIR) heating are two distinct types of infrared heating technologies, each with its own characteristics and applications.
Far Infrared Heating (FIR):
1. Far infrared radiation has longer wavelengths, which make them ideal for indoor or sheltered areas. They typically range from around 3 to 1000 micrometres.
2. FIR heaters emit lower frequency infrared waves that penetrate deeper into the skin and tissues, providing a gentle and comfortable warmth.
3. FIR heating is often used in applications such as saunas, therapy sessions, and heating pads. It's also used in some industrial processes for drying and curing materials.
4. It's known for its therapeutic benefits, including improved blood circulation, pain relief, and relaxation.
Near Infrared Heating (NIR):
1. Near infrared radiation has shorter wavelengths, typically ranging from around 0.7 to 3 micrometres.
2. NIR heaters emit higher frequency infrared waves that don't penetrate as deeply as FIR waves but are more readily absorbed by the skin's surface.
3. NIR heating is used in various applications, including physiotherapy, skincare, and heating for industrial processes like drying coatings and paint.
4. NIR therapy is believed to have benefits such as stimulating collagen production, promoting wound healing, and improving skin complexion.
10 REASONS TO INVEST IN IR HEATING
The first question most people ask is why they should invest in IR heating when they need additional heating, or they are considering a complete change of heating technology. Here are just 10 reasons to invest.
1. Simple plug-and-play installation
2. Cost-effective
3. Instant heat
4. More than just ‘white space’
5. Slimline and unobtrusive
6. Tactical, portable, task-focussed
7. Improved air quality
8. Task-focussed zone heating
9. Eco friendly
10. Smart wi-fi facility

Terms of Service
Find out more
Privacy Policy
Find out more
Shipping Policy
Find out more
Refund Policy
Find out more
Warranty
Find out more
Payment methods
Find out more